
Top
Search
People also search for:
- Home
- Why Companies Are Moving From VMs to Containers Faster Than Ever


Key Takeaways:
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to accelerate application deployment, improve scalability, and reduce infrastructure costs. For decades, Virtual Machines (VMs) were the backbone of enterprise IT infrastructure, enabling multiple isolated workloads to run on a single physical server.
However, with the rise of cloud-native applications, microservices architectures, and DevOps practices, organizations are increasingly moving from VMs to containers faster than ever. According to recent industry surveys, container adoption has grown exponentially, with Docker and Kubernetes leading the charge in modern application deployment.
This shift is not just a trend—it represents a fundamental evolution in how software is developed, deployed, and managed. Understanding why requires exploring containers vs VMs, the benefits of containerization, and the tools driving this transformation.
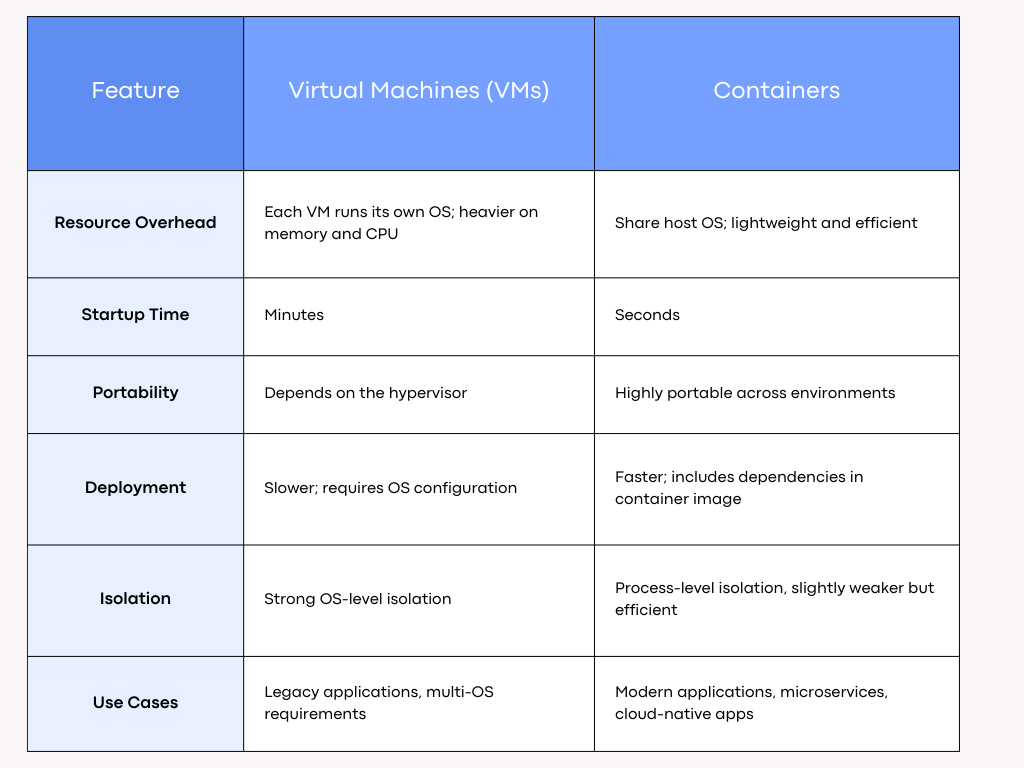
Virtual Machines are software-based simulations of physical computers. Each VM runs its own operating system and applications on top of a hypervisor, which manages resources from the host machine.
Key characteristics of VMs:
While VMs revolutionized IT by allowing multiple workloads on a single physical server, they come with limitations in speed, scalability, and resource efficiency—challenges that containers address
Containers are lightweight, portable units of software that package an application and all its dependencies. Unlike VMs, containers share the host OS kernel, which allows multiple containers to run efficiently on the same server.
Key characteristics of containers:
Docker is the most widely used containerization platform, enabling developers to create, deploy, and manage containers easily.
The efficiency, portability, and speed of containers make them increasingly attractive for enterprise adoption, especially in DevOps and cloud-native deployments.
Containerization is the process of packaging an application along with its runtime, libraries, and dependencies into a container.
Why containerization matters:
Containerization is transforming enterprise IT by enabling faster, more reliable application delivery and seamless cloud migration.
Docker has emerged as the standard platform for containerization. Docker allows developers to build, ship, and run containers efficiently.
Core benefits of Docker containers:
By using Docker containers, companies can reduce deployment times from hours to minutes, making faster deployment with containers a reality.
Running a few containers is simple, but managing hundreds or thousands requires orchestration. Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration tool, automates:
Kubernetes adoption has skyrocketed in recent years because it simplifies container management at scale, making enterprise-wide container adoption feasible.
Containers are the cornerstone of modern application deployment strategies:
By adopting containerization, enterprises can modernize legacy applications, accelerate innovation, and reduce operational complexity.
Enterprises are rapidly moving from VMs to containers due to the demands of modern application deployment, microservices architectures, and cloud-native strategies.
Key drivers of this shift include:
Transitioning from VMs to containers requires careful planning and execution. Below are key strategies for successful migration:
Identify workloads that benefit most from containerization. Stateless and cloud-native applications are ideal candidates because they are easier to break into microservices and deploy in lightweight environments. Legacy applications may need refactoring for container compatibility, as older systems often rely on tightly coupled architectures that do not translate directly into containerized environments.
Start with non-critical services to gain experience and confidence in the migration process. Once the team becomes comfortable, gradually migrate core applications while closely monitoring performance and stability. Implementing a hybrid environment during the transition helps maintain operational continuity, allowing VMs and containers to coexist until the full migration is complete.
Use Docker to build, package, and run containers efficiently across environments. To manage large-scale deployments, employ Kubernetes or Docker Swarm for orchestration and automated scaling. Additionally, use CI/CD pipelines to automate testing, deployment, and rollback, ensuring faster, more reliable release cycles.
Integrate monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or the ELK stack to gain visibility into system health: track resource usage, performance metrics, and deployment efficiency to maintain smooth operations. Continuously optimize container resource allocation to maximize cost savings and boost performance across workloads.
Educate development and operations teams on modern containerization principles to ensure they can effectively manage and maintain the new environment. Introduce best practices for DevOps and containerization integration to help teams adopt automated workflows. Encourage cross-functional collaboration to support efficient deployment pipelines and improve overall productivity.
Container adoption has accelerated across industries because organizations need scalability, efficiency, and cloud-ready environments. Below are examples of how different sectors are leveraging containerization.
Financial institutions deal with high compliance requirements and heavily dependent legacy applications. To overcome these challenges, many organizations adopt a gradual VM-to-container migration strategy supported by Kubernetes orchestration. This approach allows banks and fintech companies to deploy new financial services faster, reduce downtime, and achieve significant cost savings—all while maintaining regulatory compliance.
E-commerce businesses often struggle with massive traffic spikes during seasonal sales, festivals, or promotional events. By using auto-scaling containers in cloud environments, they can automatically handle fluctuations in demand. As a result, customers enjoy a seamless shopping experience with improved uptime, while the business benefits from reduced operational burden and better resource utilization.
Gaming and media platforms experience fluctuating user activity and require real-time performance. To meet these demands, they rely on containerized microservices paired with robust CI/CD pipelines. This setup enables rapid feature deployment, more frequent updates, and optimized resource usage—ensuring smooth gameplay, fast streaming, and enhanced user engagement.
Healthcare systems and IoT applications operate in distributed environments and must adhere to strict data-handling and privacy rules. Containers help simplify these complexities through strong orchestration and built-in security practices. This results in reliable, secure, and scalable deployment models that support medical applications, IoT devices, and real-time data flows.
As enterprises move workloads to cloud environments, containerization offers several advantages:
Orchestrating containers at scale is essential for enterprise adoption. Kubernetes has become the de facto standard, but other tools also play important roles:
| Tool | Key Features | Use Case |
| Kubernetes | Automated scaling, self-healing, rolling updates, service discovery | Large-scale container deployments, hybrid clouds |
| Docker Swarm | Simple orchestration, native Docker integration | Small-to-medium container clusters |
| Openshift | Enterprise-grade Kubernetes, developer-friendly | Enterprises needing security, compliance, and CI/CD integration |
| Rancher | Multi-cluster management | Managing multiple Kubernetes clusters across clouds |
Why orchestration matters:
DevOps and containerization are complementary, enabling faster, more reliable software delivery.
By combining containerization with DevOps practices, organizations achieve faster deployment, improved performance, and scalable architectures.
Microservices break applications into smaller, independently deployable services, which aligns naturally with containerization:
This synergy explains why container adoption is accelerating at a record pace among enterprises pursuing microservices.
One of the primary reasons companies are rapidly shifting from VMs to containers is the significant performance boost. Containers are designed to run more efficiently, scale faster, and offer a smoother deployment experience across environments.
Lightweight Execution
Containers share the host OS kernel, eliminating the need to run multiple full operating systems. Because of this lightweight approach, applications launch much faster and consume fewer system resources. This efficiency enables teams to run workloads quickly and cost-effectively.
Optimized Resource Usage
Compared to traditional VMs, containers manage memory and CPU far more efficiently. This allows enterprises to run a larger number of applications on the same hardware without suffering performance drops. As a result, organizations gain higher workload density and reduced operational costs.
Faster Deployment Cycles
With containers, developers can package applications along with all their dependencies, ensuring consistency across development, testing, and production. This eliminates environment-specific issues and dramatically reduces deployment times—from hours in a VM environment to mere minutes or even seconds with containers.
Scalable Microservices Architecture
Containers support microservices architectures by allowing each service to run independently. This means that every microservice can be scaled separately based on demand, helping eliminate bottlenecks and significantly enhancing application responsiveness.
While containers offer many advantages, they introduce unique security considerations. Proper practices are essential for safe deployment:
By following these practices, organizations can securely adopt containers without compromising speed or flexibility.
The future of enterprise IT is container-driven, with several emerging trends shaping adoption:
These trends indicate that containerization will become the standard for modern application deployment, far outpacing traditional VMs.
Containerization has become a foundational pillar of modern enterprise IT. By offering lightweight, portable, and scalable environments, containers enable organizations to build, deploy, and manage applications faster and more efficiently than traditional infrastructure models. Technologies like Docker, Kubernetes, and advanced orchestration tools have moved containerization from a developer convenience to an enterprise-grade strategy.
For businesses, the impact is clear: faster deployment cycles, improved application performance, better resource utilization, and reduced infrastructure costs. When paired with strong security and compliance practices, containerized environments can remain both agile and secure at scale.
Looking ahead, the rise of serverless architectures, AI-driven monitoring, multi-cloud strategies, and edge computing further reinforces one reality — containerization is not a passing trend. It is set to dominate how enterprises design, operate, and scale their digital systems in the years to come.
Q1: Why are companies moving from VMs to containers faster than ever?
A: Containers are lightweight, start quickly, scale efficiently, reduce infrastructure costs, and integrate seamlessly with modern DevOps and cloud-native architectures.
Q2: Are containers more secure than VMs?
A: Containers are secure when best practices are followed, but they share the host OS, so runtime monitoring and vulnerability scanning are critical.
Q3: Can all applications be containerized?
A: Stateless, microservices, and cloud-native applications are ideal. Legacy monolithic applications may require refactoring or hybrid approaches.
Q4: What is the role of Kubernetes in container adoption?
A: Kubernetes orchestrates container deployment, scaling, self-healing, and monitoring, making enterprise-level container adoption feasible.
Q5: How do containers improve performance?
A: Containers eliminate VM overhead, allow faster startup times, optimize CPU and memory usage, and enable independent scaling of microservices.
Q6: How do companies migrate from VMs to containers?
A: Through assessment, phased migration, Docker and orchestration tools, CI/CD integration, monitoring, and team training.
We bring development and operations together seamlessly.Improving deployment speed, reliability, and infrastructure resilience.
Consult DevOps Experts
I am a Software Engineer specializing in both full-stack development and DevOps. I work across the MERN stack, UI/UX, and API development to build clean, scalable applications—while also designing the DevOps systems that keep them fast, stable, and easy to deliver. At Apidots, I contribute end-to-end: from architecting features and writing efficient code to implementing CI/CD pipelines, automating workflows, and ensuring smooth, reliable deployments. I enjoy bridging the gap between development and operations, creating solutions that are not only well-built but also easy to maintain, monitor, and scale. I’m motivated by problem-solving, continuous improvement, and building products that combine strong engineering with seamless user experience.